1 Introduction
The rapid development of the automobile market is bound to drive the development of related industries. As an indispensable comfort function for automobiles, automotive air conditioners have also encountered unprecedented development opportunities. The car air conditioning system is a comfortable device that realizes cooling, heating, ventilation and air purification of the air in the cabin. It can provide passengers with a comfortable riding environment, reduce the driver's fatigue strength and improve driving safety. Air-conditioning units have become a sign of the perfection of car functions.
2 Car air conditioning working principle
2.1 Vehicle refrigeration system
The most basic and complex automotive air conditioning is the in-vehicle refrigeration system. The compressor power of a modern on-board refrigeration system is driven by a motor. The refrigeration system consists of a compressor, a condenser, a receiver drier, an expansion valve, an evaporator, and a blower, as shown in Figure 1. Copper pipes (or aluminum pipes) and high-pressure rubber pipes are connected between the components of the vehicle refrigeration system to form a closed system. When the refrigeration system is in operation, the refrigerant circulates in this closed system in two states of compression and expansion.
2.2 Refrigerant cycle refrigeration process
The refrigerant (refrigerant) cycle of a refrigeration system is divided into four basic processes:
(1) Compression process: The compressor sucks in the low-temperature and low-pressure refrigerant gas at the outlet of the evaporator, and compresses it into a high-temperature and high-pressure gas-eliminating compressor.
(2) Heat dissipation process: The high temperature and high pressure superheated refrigerant gas enters the condenser. Due to the pressure and temperature decrease, the refrigerant gas condenses into a liquid and discharges a large amount of heat.
(3) Throttling process: the refrigerant liquid with higher temperature and pressure passes through the expansion device, and the volume becomes larger, the pressure and temperature drop sharply, and the expansion device is discharged in a mist (fine droplets).
(4) Endothermic process: The misty refrigerant liquid enters the evaporator, so the boiling point of the refrigerant is much lower than the temperature inside the evaporator, so the refrigerant liquid evaporates into a gas. The surrounding heat is absorbed in a large amount during the evaporation process, and then the low-temperature low-pressure refrigerant vapor enters the compressor again.
The refrigerant expansion and compression process is carried out continuously, and the purpose of reducing the temperature of the air around the evaporator can be achieved.
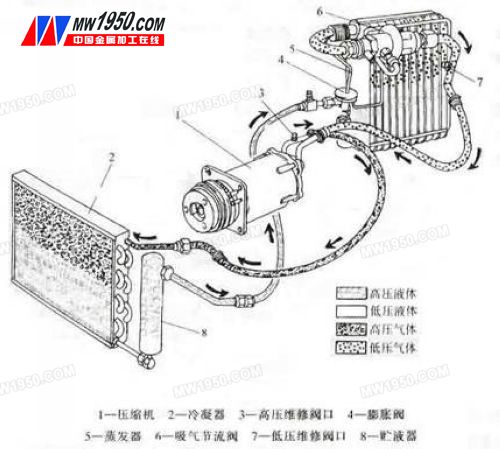
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the refrigeration system
| 1 | 2 | 3 | Next page |
Medicinal Activated Carbon,Activated Carbon For Medicine,Activated Carbon
Wood Based Activated Carbon,Coal Based Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. , http://www.nsactivatedcarbon.com