(1) When a flying or falling object hits the head;
(2) When the operator falls from a height of 2m or more;
(3) When there is a possibility of electric shock on the head;
(4) When walking or working in a low position, the head may collide with a sharp, hard object.
Wear safety helmets to meet the standards, use to meet the requirements. If it is worn and used incorrectly, it will not provide sufficient protection. Generally should pay attention to the following matters:
(1) Before wearing a helmet, adjust the rear cap adjustment belt to the proper position according to your own head type, and then fasten the elastic strap inside the cap. The elasticity of the cushioning pad is regulated by the strap. The vertical distance between the top of the head of the person and the top of the cap body is generally between 25 and 50 mm, and at least not less than 32 mm. In this way, it can be ensured that when the impact is applied, the cap body has enough space for cushioning, and it is usually beneficial to the ventilation between the head and the cap body.
(2) Do not wear a hard hat or wear a brim behind your head. Otherwise, the protective effect of the helmet on the impact will be reduced.
(3) The lower tie of the helmet must be buckled under the jaw and fastened tightly. This will not be blown off by strong winds, or it will be touched by other obstacles, or the helmet will come off due to the back and forth swing of the head.
(4) In addition to the cap lining inside the cap body, some of the helmet heads also have small holes for ventilation. However, do not casually open the hole for ventilation during use. This will reduce the strength of the cap body.
(5) Due to the safety helmet, it will gradually be damaged during use. Therefore, it is necessary to check regularly to check for cracks, undercuts, cracks, and wear. If any abnormalities are found, they must be replaced immediately and they must not be used again. Any severely hit, cracked hard hat, whether or not there is any damage, should be scrapped.
(6) It is forbidden to use a safety helmet with only the lower jaw attached to the cap shell, ie, a safety cap with no buffer layer inside the cap.
(7) The construction personnel shall not take off the helmet, set it aside, or use it as a cushion during the on-site operation.
(8) Because the safety helmet is mostly made of high-density low-pressure polyethylene plastic, it has the properties of hardening and blemishes. So it is not easy to expose to sunlight for a long time.
(9) Newly-collared helmets are first to check whether there is a labor department's permission for production and product certification, and whether damage, uneven thickness, and buffer layers, adjustment belts, and elastic belts are complete and effective. Does not meet the requirements of the immediate exchange.
(10) Wear safety helmets for on-site indoor work. Especially when working in the room, wear safety helmets because the helmets can not only prevent collisions but also provide insulation.
(11) Peacetime helmets should be kept clean and tidy, and they must not touch the fire source. Do not paint on any of them. Do not sit on stools to prevent loss. If lost or damaged, it must be replaced or replaced immediately. No helmets are allowed to enter the construction site.
Second, the seat belt
Electric power construction site, high work, overlap and crossover operations are numerous. In order to prevent the operator from falling down at a certain height and position, the operator must be fastened with a seat belt when working at height and height. The use and maintenance of seat belts have the following requirements:
(1) The role of seat belts must be emphasized in thinking. Numerous examples demonstrate that the seat belt is a "life-saving belt." However, a small number of people feel that it is troublesome to wear a seatbelt. It is inconvenient to walk up and down, especially some livelihoods and temporary activities. They think that “there is a time to live with a safety beltâ€. As everyone knows, the accident occurred in a moment, so high-level operations must be required to fasten the seat belt.
(2)Before using the seatbelt, check that the cord is not deteriorating, if there is any crack in the retaining ring, and if the snap-in spring is good.
(3) In high places such as seat belts, there shall be no fixed hangers, and appropriate strength wire ropes or other methods shall be used. It is forbidden to hang the seatbelt on a moving or with a sharp angle or an unstable object.
(4) high hanging low use. Hanging a seat belt high, people working underneath is called high hanging. This is a relatively safe and scientific method of hanging. It can reduce the actual impact distance when a crash occurs. The opposite is the low hanging high. It is the safety belt hanging in the low place and the person working on it. This is a very unsafe method of attachment, because when the fall occurs, the actual impact distance will increase, and both the person and the rope will be subject to a greater impact load. Therefore, seat belts must be kept high and low, and high-risk use should be avoided.
(5) The seat belt must be hung on a firm member or object. To avoid swinging or colliding, the rope cannot be knotted and the hook should be hung on the connecting ring.
(6) The seat belt rope protection cover should be kept intact to prevent the rope from being worn out. If it is found that the protective sleeve is damaged or peeled off, it must be used after adding a new one.
(7) It is strictly prohibited to use the seat belt without authorization. If a long rope with 3m or more is used, a buffer must be added, and the parts must not be removed.
(8) Before using the seat belt, check whether all parts are intact. Safety belts should be maintained and kept after use. Always inspect the seat belt sewing section and the hook section, and check the rifling thread for cracks and damage.
(9) When the seat belt is not in use, it should be properly kept. Do not touch high temperature, open flame, strong acid, strong alkali or sharp objects, and do not store it in a damp warehouse.
(10) Safety belts should be inspected once after two years of use. Frequent use should be performed visually. Abnormalities must be replaced immediately. Regular seat belts or used seat belts are not allowed to continue to be used.
Third, protective clothing
Electric power construction workers on the construction site should wear work clothes. Welders’ uniforms are generally white, and other types of workwear are not limited by color. Protective clothing has the following types:
(1) Overall protective overalls;
(2) Antivirus uniforms;
(3) Acid resistant work clothes;
(4) Fireproof work clothes;
(5) Insulation work clothes;
(6) ventilation cooling work clothes;
(7) Water cooling working clothes;
(8) Anti-radiation work clothes;
(9) Labor protection raincoats;
(10) Ordinary work clothes.
The wearing requirements of protective clothing for workers on construction sites are:
(1) Workers must wear overalls while working;
(2) The cuff must be tight when operating the rotating machine;
(3) Personnel engaged in special operations must wear special protective clothing;
(4)Welder uniforms should be made of white canvas.
Fourth, protective glasses
Material particles and debris, sparks and heat flow, dazzling light and smoke can cause eye damage. In this way, it is necessary to select and use safety glasses according to the different protection objects.
(1) There are three types of eye-protective goggles:
1 hard glass goggles;
2 Colloid-bonded vitreous goggles (cracked, not splashed when impacted, hit and broken);
3 steel mesh goggles. They can prevent the impact of metal fragments or swarf, sand dust, stone chips, concrete chips and other spatters on the eyes. Metalworking, concrete chiseling, and hand grinder operations are suitable for wearing such flat goggles.
(2) UV protection goggles and radiation protection masks for UV protection and strong light. The radiation protection mask used for welding work shall be made of non-conductive material, and the observation window, filter, and protection sheet shall have the same size and no gap. The color of the goggles is a mixture of colors, preferably blue, green, and gray.
(3) The anti-hazardous liquid goggles are simple and are mainly used to prevent damage to the eyes caused by acids, alkalis and other liquids and other dangerous injections and chemicals. General lenses are made of ordinary glass and frames are made of non-metallic, corrosion-resistant materials.
(4) Adding a certain amount of lead-glass goggles made of metallic lead to the glass of the lens is mainly to prevent X-rays from damaging the eyes.
(5) Anti-dust, smoke, and all kinds of toxic glasses with slight toxicity or weak irritant must be sealed, covered with no vents, tightly in contact with the face, frames must be resistant to acids and alkalis.
Fifth, protective shoes
More types of protective shoes, such as leather safety shoes, anti-static rubber-soled shoes, plastic anti-hit safety shoes, insulated leather shoes, low-voltage insulating rubber shoes, acid and alkali resistant shoes, acid and alkali rubber boots, acid and alkali plastic molded boots, high temperature Protective shoes, anti-puncture shoes, welding protective shoes, etc. It should be used according to the different places and contents. Electric power construction and construction sites commonly used insulation boots (shoes), welding protective shoes, acid and alkali resistant rubber boots and leather safety shoes. The requirements for insulating shoes are:
(1) Must be used within the specified voltage range;
(2) The rubber parts of the insulating shoes (boots) are not damaged, and a preventive test is made every six months;
(3) It must not be used as an auxiliary safety device when it is immersed in water, oil, acid, or alkali.
Sixth, protective gloves
Most of the work on the construction site is done by both hands. This determines that the hand is often in danger. The safety of the opponent mainly depends on gloves. When using protective gloves, after analyzing the parts, equipment, and work conditions, select gloves made of suitable materials that are easy to operate, so as to protect them. But for jobs that require fine-tuning. Wearing protective gloves is inconvenient to operate, especially for operators using drilling machines, milling machines and conveyors, and in areas where there is a risk of pinching. If gloves are used, there is a danger of mechanical entanglement or pinching. Therefore, personnel engaged in these operations are strictly prohibited from using protective gloves. The following are the commonly used protective gloves on the construction site:
(1) Labor protection gloves. It has the function of protecting hands and arms, and workers usually use such gloves when working.
(2) Insulating gloves for live working. According to the voltage to select the appropriate gloves, check the surface for cracks, sticky, brittle and other defects, if abnormal use is prohibited.
(3) Acid and alkali resistant gloves. Primarily used for gloves worn when exposed to acids and alkalis.
(4) Rubber oil resistant gloves. It is mainly used for gloves that are exposed to a variety of mineral oils, vegetable oils, and fatty clusters.
(5) Welder's gloves. For the protective gloves worn in the electric and fire welding industry, the presence or absence of incompleteness on the surface of leather or canvas should be checked. If there are any defects, use of the protective gloves must not be used. The gloves should be of sufficient length and the wrists should not be exposed outside.
Seven, common safety protective equipment inspection methods
The commonly used safety protective gear must be carefully checked and tested. Is there any debris on the safety net, whether it is damaged by falling objects or damaged by lifting objects? After the helmet is struck by an object, there is a crack or the like. Frequent inspection of safety gear as required
(1) Hard hat: 3kg heavy steel ball, which is not damaged when impacted from a height of 5m vertical free fall. Apply a semi-circular human head model to the wood during the test, and tie the buffered elastic band inside the helmet to the model. . This method can be used for hard hat tests made of various materials. The inspection cycle is once a year.
(2) Seat belt: According to the national regulations, the factory test is to take an object with a load of 120kg. The seat belt is impacted from an overhead frame of 2 to 2.8m. Each component is qualified without damage. According to actual conditions, the construction unit can adopt some practical measures to meet the local conditions and meet the heavy load standards of the test load. Some of the methods that are often used by construction agencies are the use of sacks, wood chips, etc. as fillers and iron, to meet the heavy standards of test loads. With a shelf designed for experiments, dynamic and static load tests were performed. Nylon belt accessories extreme tensile index is: belt 1200 ~ 1500kg, straps 700 ~ 1000 kg, safety rope 1500 kg, hook ring 1200 kg, fixed clip 60 kg, legs with 700 kg. The load test requirements for seat belts are: The construction unit should periodically perform static load tests on the seat belts. Test load is 225 kg, hanging 5min, check whether the deformation, rupture, etc., and make records. The belt inspection cycle is: Before each seat belt is used, it must be carefully checked. Two years after the new seat belts were used for spot checks, the old seat belts were sampled every six months. It should be noted that any safety gear that has been tested must not be reused.
(3) The inspection of personal protective equipment must also pay attention:
1) Whether the product has a product produced by a "production license" unit;
2) Whether the product has a "product certificate";
3) whether the product meets the relevant quality requirements of the product;
4) Is the product specification and technical performance consistent with the protection requirements of the job?
Optical Flats mirrors are ideal for a variety of applications including interferometry, imaging systems, laser applications, optical path folding, and autocollimation. These mirrors are available in a variety of coating and substrate options, along with surface flatness options of λ/10 and λ/20. Fused Silica, is optically clear and features excellent resistance to abrasion and high durability, making it the best choice for applications in harsh environments.
The mirrors are available in circular, square, and rectangular dimensions. Rectangular first surface mirrors are ideal for applications requiring the mirror to be mounted at 45° in order to produce a 90° bend in the light path.
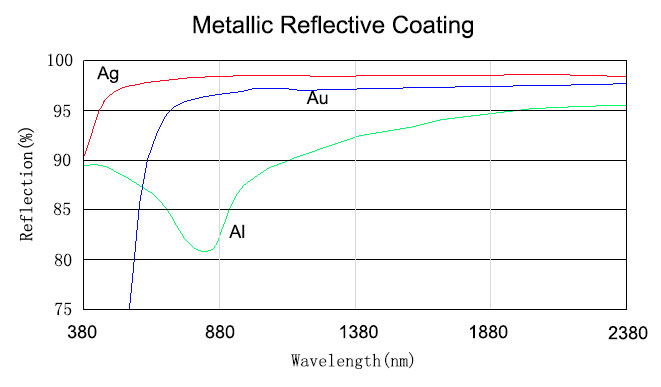
Protected metallic coatings provide a moderate level of reflection over a very broad spectral range and are widely used as mirrors. These coatings are protected by a thin layer of dielectric material in order to make them durable. Enhanced metallic coatings provide greater reflection across the operating band width. These coatings are enhanced by adding a multilayer dielectric stack. Metal coatings will modify the state of polarization of an incident beam of light and are therefore inappropriate for most polarization sensitive applications.
+
Optical Glass Flat Mirror,Optical Glass Protective Flat Mirror,Al Protective Mirror,Aluminium Flat Mirror
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.realpoooptics.com